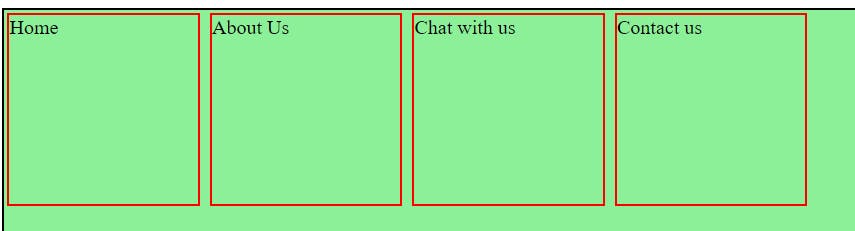
There are five different position values:
Absolute
Fixed
Relative
Sticky
Static
Absolute:
Absolute is a very powerful positioning property. It allows you to place any page element exactly wherever you want. We can use attributes like a top, bottom, left, and right to place the element.
In the absence of any parent element, the HTML element will be placed relative to the page.
position: absolute;
top: 34px;%
left: 134px;
Result:
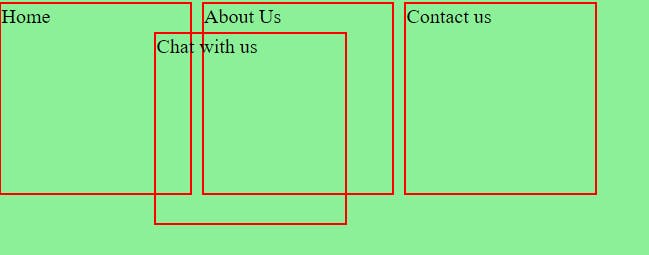
Fixed:
Positions the element relative to the browser window. The element with position fixed, positioned relative to its viewport and gets fixed at a position and it always stays in the same place even if the page is scrolled.
position: fixed;
right: 20px;
bottom: 2px
Result:

Relative:
The element is positioned according to the normal flow of the document, and then offset relative to itself based on the values of top, right, bottom, and left.
position: relative;
left: 20px;
top: 10px;
Result:
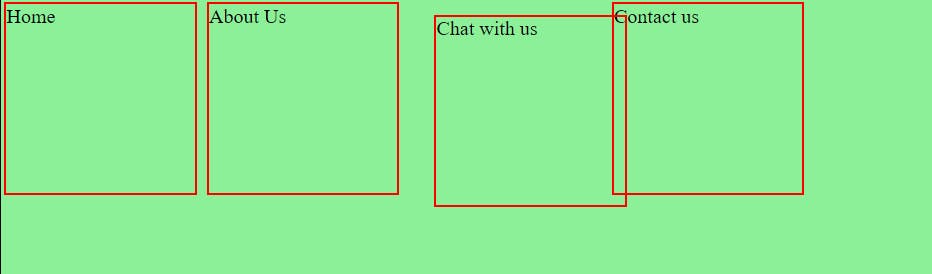
Sticky:
Positions the element relative to the user's scroll position. An element with a position fixed will remain stuck to a specific position even after the page is scrolled. This position property is used when we want to keep an HTML element at a fixed spot no matter where on the page the user is.
position: sticky;
top: 30px;
Result:
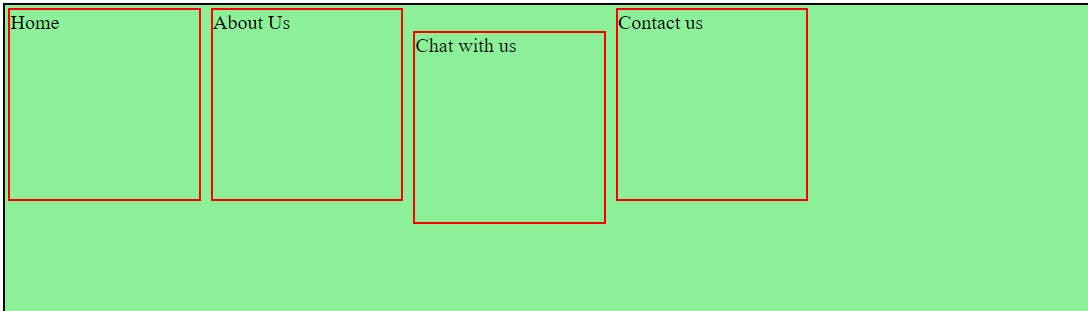
Static:
Static positioning is the default for every HTML element. The element is positioned according to the normal flow of the document. The top, right, bottom, left, and z-index properties have no effect.
#position static {
height: 100px;
}
Result: