In this article, I'll be explaining the most popular CSS property, known as Flexbox. Let's begin the learning process with examples.
Firstly, the basic syntax to use flexbox:
.container{
display: flex;
}
Output:
The above syntax will enable all the features of the CSS flex property.
Note that CSS columns have no effect on a flex container.
1. flex-direction:
This property specifies the direction in which the main axis runs.
.container{
flex-direction: row | row-reverse | column | column-reverse;
}
- row: Flex items will be laying out from left to right and this is by default.
- row-reverse: this is exactly opposite to i.e., from right to left.
- column: this is the same as the row but top-bottom.
- column-reverse: this is the same as the row but bottom-top.
flex-direction: row-reverse
Output:

2. flex-wrap:
This property allows the items to wrap as needed. Flex items try to fit on one line.
.container {
flex-wrap: nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse;
}
- nowrap: all the items will be on one line. This is by default.
- wrap: all the items will be wrapped into multiple lines from top to bottom.
- wrap-reverse: this is the same as a wrap but from the bottom-top.
flex-wrap: wrap
Output:
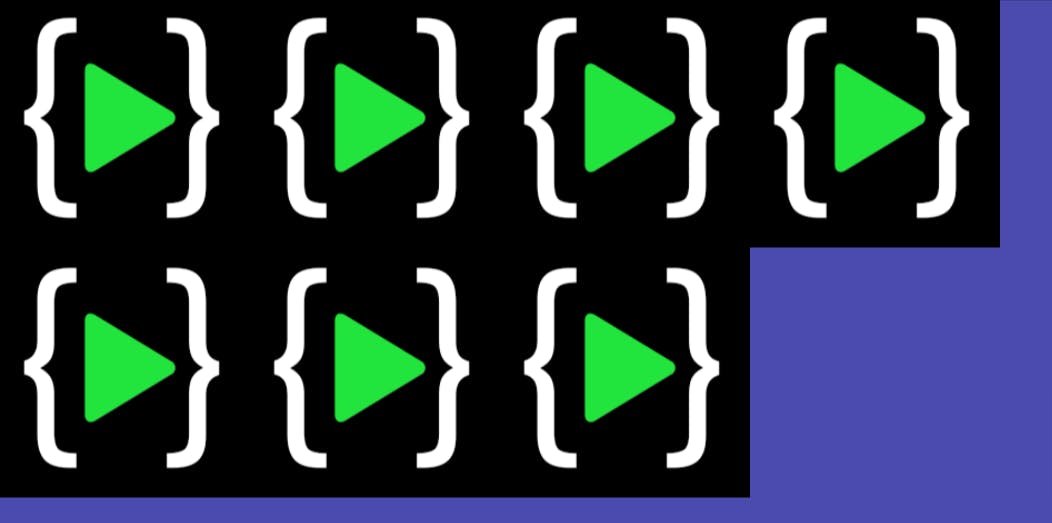
3. justify-content:
This property allows for aligning the items along the main axis.
.container {
justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | space-evenly |
}
- flex-start: items are packed toward the start of the flex direction. This is by default.
- flex-end: items are packed toward the end of the flex direction.
- space-between: items are evenly distributed in the line; the first item is on the start line, and the last item is on the end line.
- space-around: items are evenly distributed in the line with equal space around them.
- space-evenly: items are distributed so that the spacing between any two items is equal.
justify-content: center
Output:

4. align-items:
This property allows for aligning the items along the cross axis(vertical axis).
.container {
align-items: stretch | flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | start | end |
}
- stretch: stretch to fill the container. This is by default.
- flex-start/start: items are placed at the start of the cross axis.
- flex-end/end: items are placed at the end of the cross axis.
- center: items are placed at the center of the cross axis.
- baseline: items are aligned such as their baselines align.
align-items: flex-start
Output:

5. align-self:
This property allows for aligning one specific item along the cross axis.
.element-3 {
align-self: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;
}
All the property of align-self is the same as of align-items.
.element-3 { align-self:center }
Output:
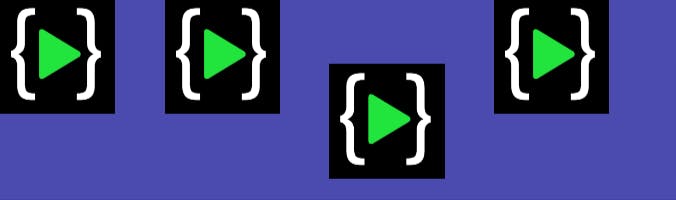
6. align-content:
This property defines how each line is aligned within a flexbox container. It only applies if flex-wrap: wrap is present and if there are multiple lines of flexbox items.
.container {
align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | space-evenly | stretch |
}
- flex-start/start: items packed to the start of the container.
- flex-end/end: items packed to the end of the container.
- center: items packed to the center of the container.
- space-between: items evenly distributed; the first line is at the start and the last line is at the bottom.
- space-around: items evenly distributed maintaining equal space around each line.
- space-evenly: items evenly distributed maintaining equal space around them.
align-content: center
Output:

7. gap:
gap property is not only for flexbox, it works in the grid and multi-column layout as well.
This property controls the gap between the flex items. It only controls the gap between the items not on the outer edges.
.container {
display: flex;
gap: 10px;
gap: 10px 15px;
row-gap: 10px;
column-gap: 15px;
}
Output:

8. order:
This property targets individual items and changes where they appear in the visual order with the order property.
.container :nth-child(1) {
order: 3;
}
.container :nth-child(2) {
order: 1;
}
.container :nth-child(3) {
order: 2;
}

9. flex-grow:
This property defines the ability of a flex item to grow if necessary. It dictates what amount of the available space inside the flex container the item should take up. Flex-grow is basically for what percent width will get this element considered to others in max-width.
.item-3 {
flex-grow: 2;
}
Output:

Flexbox has so many properties but in this blog, I covered the most used and common flexbox properties which are regularly used. If you are interested to know more about flexbox, Then follow the below links:

